IT for Manufacturing - About Present and Future
Terms like Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory have become an integral part of the discussion about the digitalization of the manufacturing industry. These technologies have developed rapidly in recent years and led to new user requirements. But how exactly have these concepts changed and which technologies are actually being used in practice? What are the biggest challenges in introducing new digital solutions and what factors are crucial for their success?
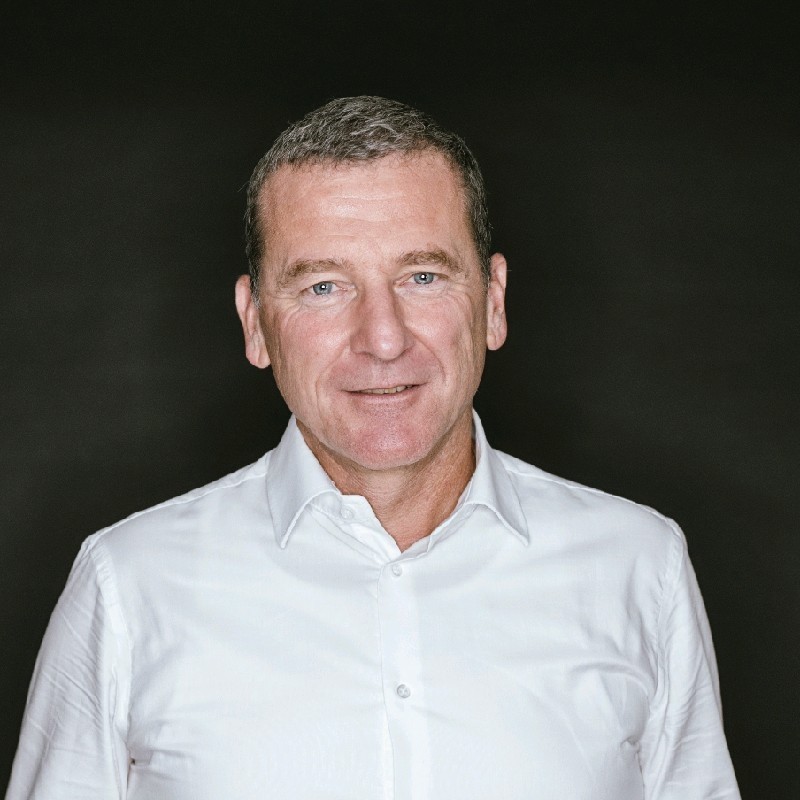
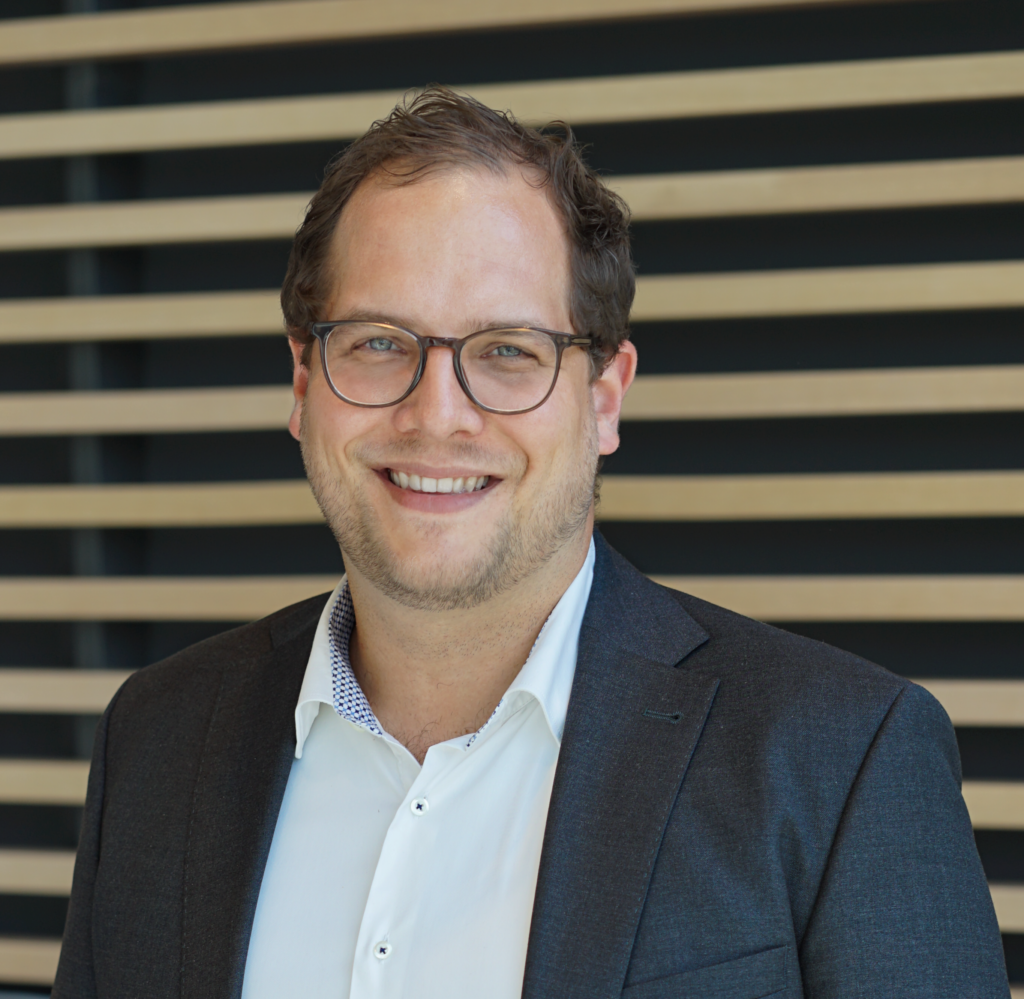
Cyrill Schmid, Managing Partner of topsoft – the largest independent platform for digital business in Switzerland – sheds light on these central questions in an interview with Raphael Prior, Managing Director of our Swiss location.




Terms like Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory have become an integral part of the discussion about the digitalization of the manufacturing industry. These technologies have developed rapidly in recent years and led to new user requirements.
But how exactly have these concepts changed and which technologies are actually being used in practice? What are the biggest challenges in introducing new digital solutions and what factors are crucial for their success?
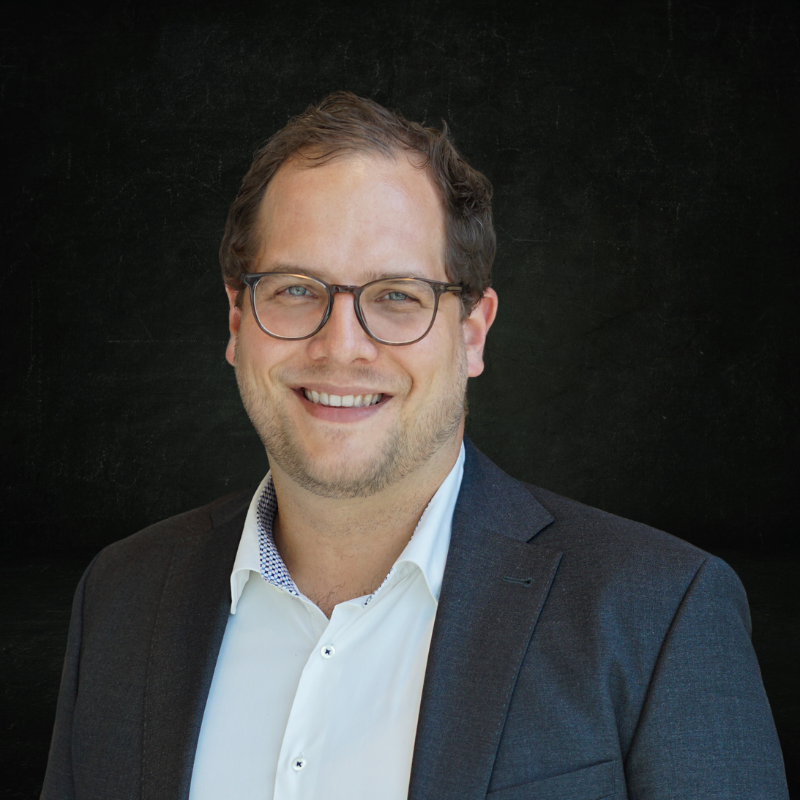


Cyrill Schmid, Managing Partner of topsoft – the largest independent platform for digital business in Switzerland – sheds light on these central questions in an interview with Raphael Prior, Managing Director of our Swiss location.
Development and Change
Cyrill Schmid: For several years now, I40, Smart Factory, etc. have been key topics in digitalization. How have these concepts and technologies evolved and which user requirements have changed the most?
Raphael Prior: In recent years, Industry 4.0 and Smart Factory have developed significantly. Initially, the focus was on networking and automation; today, data utilization and AI are crucial. User requirements are increasingly evolving from simple automation to intelligent, self-optimizing systems. Companies demand real-time analyses, predictive maintenance and flexible, adaptable production processes. Faster responsiveness to market changes and increased efficiency pressure while maintaining product quality are driving this development.
Application and Reality
Cyrill Schmid: Which Industry 4.0 or Smart Factory technologies are your customers currently using and in which areas are they most frequently applied?
Raphael Prior: Our customers are increasingly focusing on fully automated manufacturing planning and optimization (MSO) in IFS CloudTM. Simulations and Digital Twins improve production monitoring, detect failures early and plan maintenance proactively. Through external data such as demand forecasts and supplier information, production capacities are optimized and bottlenecks identified early. This combination of MSO, Predictive Maintenance and Digital Twins enables competitive optimization of manufacturing and warehouse processes.
Challenges and Success Factors
Cyrill Schmid: What are the biggest challenges in introducing new technologies in digital manufacturing and what critical success factors do you see?
Raphael Prior: From our experience, successful implementations are characterized particularly by effective change management and optimal technical infrastructure. The digital age places high demands on employees and requires acceptance of process changes. Especially for larger projects, a specialized change manager can support and relieve the organization. The goal is a swift implementation of core processes along the value chain. An easily configurable ERP system with modern low-code integrations supports this.
Future Trends
Cyrill Schmid: Which trends do you see as shaping the development of digital manufacturing in the next 5-10 years?
Raphael Prior: Key themes we can expect here are increased integration of AI and machine learning for data pattern recognition – moving away from the traditional static approach towards dynamic planning. Digitalization in manufacturing will need to adapt to new generations of employees. Regulations to minimize environmental impact and sustainability will also confront companies with disassembly, recycling and a shift towards a circular economy. Here too, the right technology will play a crucial key role.
Read more about the focus topics Smart Factory & Industry 4.0, Artificial Intelligence and ERP for manufacturing in the current issue 24-2 of the topsoft trade magazine.